Introduction
In a rapidly changing world where the pace of innovation shapes our daily lives, the design thinking process emerges as a beacon of hope amidst the complexity of modern challenges. Beyond a mere methodology, it represents a transformative mindset, igniting creativity and inspiring user-centric approaches to navigate even the most daunting of issues.
At its core, design thinking embodies a philosophy deeply rooted in understanding human needs, championing iterative processes, and fostering collaboration within diverse design teams. This holistic approach transcends traditional problem-solving frameworks, offering a nuanced perspective that empowers individuals and organizations to confront and conquer the most wicked problems of our time.
In an era defined by interconnectedness and unprecedented technological advancement, the principles of design thinking serve as a guiding light, illuminating pathways to innovative solutions and sustainable progress. By embracing empathy, curiosity, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, practitioners of design thinking embark on a journey of exploration and discovery, uncovering insights and opportunities hidden beneath the surface of complexity.
In today’s dynamic landscape, where disruptive forces and unforeseen challenges abound, the relevance of design thinking extends far beyond the realms of product development and business strategy. It permeates every aspect of our lives, from healthcare and education to sustainability and social justice, offering a versatile toolkit for tackling multifaceted issues with creativity and compassion.
As we stand at the precipice of a new era defined by uncertainty and possibility, the principles of design thinking serve as a lodestar, guiding us towards a future where innovation thrives, and human needs remain at the forefront of our collective consciousness. Through collaboration, experimentation, and a steadfast commitment to continuous improvement, we unlock the transformative potential of design thinking, harnessing its power to shape a world that is more inclusive, more equitable, and more resilient for generations to come.

Step 1: Understanding Human Needs – The Foundation of Design Thinking Process
Human-Centered Design: Design thinking begins with a profound appreciation for human needs. It’s about stepping into the shoes of the user, understanding their challenges, and empathizing with their experiences. By prioritizing human-centric ways, design thinkers can develop solutions that truly resonate with the people they serve.
User Research: Before diving into the design process, it’s crucial to conduct thorough user research. This involves engaging with real people, observing their behaviors, and uncovering insights into their needs and pain points. Whether it’s through interviews, surveys, or observation sessions, user research lays the groundwork for informed decision-making throughout the design process.
Empathy Maps: Empathy is the cornerstone of human-centered design. Empathy maps allow design teams to visualize and empathize with users’ experiences, emotions, and motivations. By taking a closer look at users’ perspectives, teams gain valuable insights that inform the design process and drive the creation of solutions that truly make a difference.
Design thinking, as championed by Tim Brown at Stanford University, emphasizes the importance of viewing problems from different perspectives and exploring diverse ideas. By understanding the needs of users and embracing a user-centric approach, design teams can embark on a journey towards innovative solutions that not only address specific problems but also enhance the overall user experience.
In the subsequent sections, we’ll delve deeper into the key steps of the design thinking process, exploring how iterative approaches, ideation sessions, prototyping, and testing stages contribute to the creation of impactful solutions. Join us as we unravel the stages of design thinking and uncover the secrets behind its transformative power.
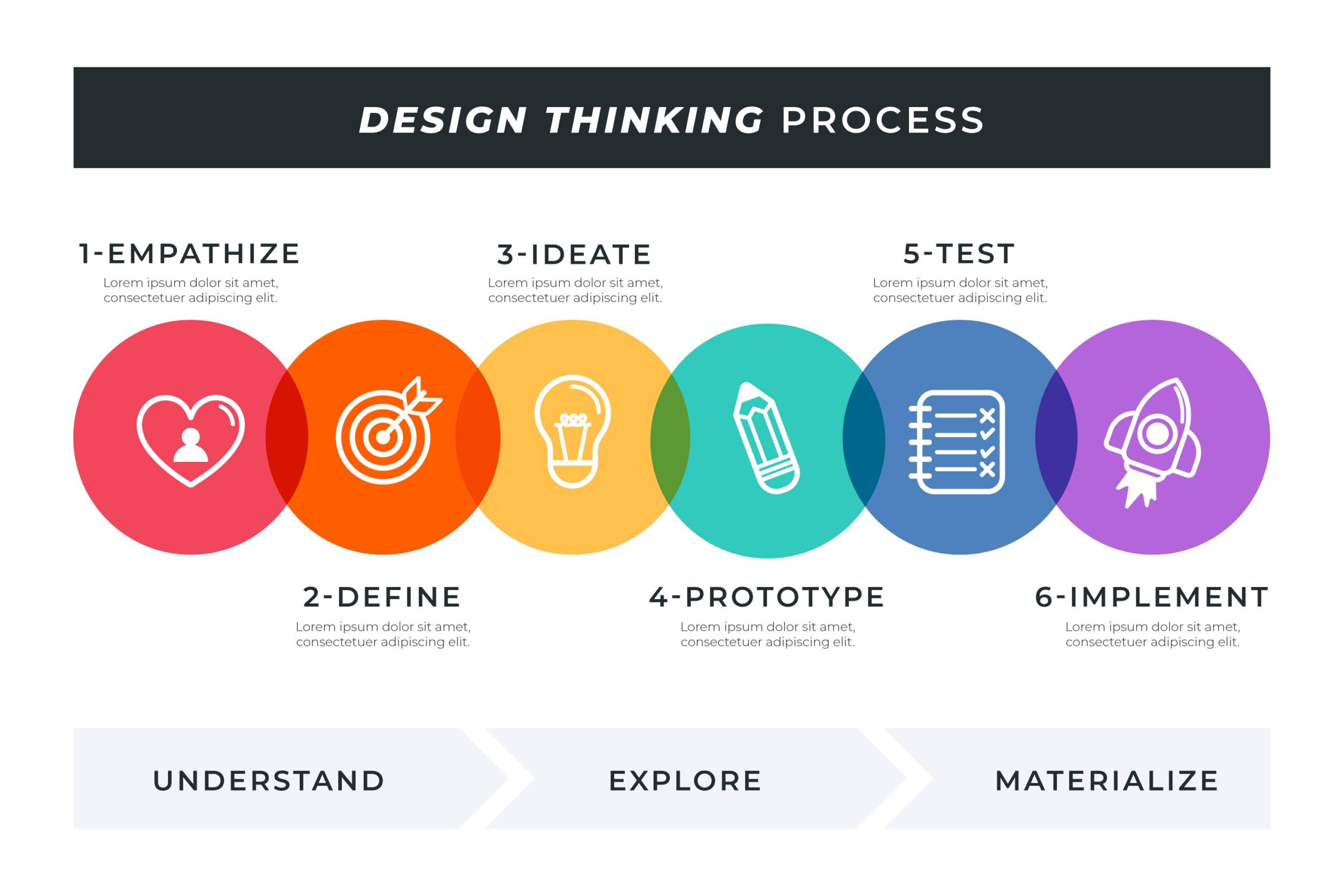
Step 2: Defining the Problem – Setting the Stage for Innovation
In the intricate dance of design thinking, defining the problem is akin to setting the stage for a captivating performance of innovation. It’s the crucial first step that shapes the entire design process and guides the quest for solutions to complex problems.
Clear Problem Statement: At the heart of problem definition lies the art of crafting a clear and actionable problem statement. This statement serves as a beacon, guiding the efforts of the design team towards a common goal. A well-defined problem statement articulates the specific issue at hand and provides a roadmap for exploration and solution.
Asking the Right Questions: In the pursuit of clarity, design thinkers must be adept at asking the right questions. These questions probe beneath the surface, unraveling the intricacies of the problem and shedding light on its underlying causes. By asking the right questions, design teams gain deeper insights into the problem landscape and uncover hidden opportunities for innovation.
Identifying Wicked Problems: Not all problems are created equal. Some defy simple solutions and lurk in the realm of wickedness. Wicked problems are complex, multifaceted challenges that resist conventional approaches. In the face of such formidable adversaries, design thinking advocates for a solution-based approach that embraces ambiguity and thrives on iteration.
Step 3: Ideation – Generating Creative Ideas
With the problem defined and the stage set, it’s time for the creative magic of ideation to unfold. Ideation is the fertile ground where seeds of innovation are sown, nurtured, and cultivated into bold and imaginative solutions.
Ideation Sessions: Ideation sessions are the crucible of creativity, where design teams come together to explore, brainstorm, and generate a plethora of ideas. These sessions are marked by an atmosphere of open-mindedness, curiosity, and collaboration, where no idea is too outlandish or absurd to be considered.
Divergent Thinking: At the heart of ideation lies the principle of divergent thinking – the ability to explore a multitude of possibilities and perspectives. Design thinkers are encouraged to think beyond the confines of convention, to challenge assumptions, and to explore uncharted territories of possibility.
Iterative Approach: Ideation is not a one-time event but rather a continuous and iterative process. Ideas are refined, reshaped, and reimagined through a cycle of feedback and iteration. Each iteration brings design teams closer to the elusive goal of discovering the best solution – the solution that resonates most deeply with the needs of the user and the objectives of the project.
In the next sections, we’ll delve deeper into the stages of prototyping, testing, and implementation, exploring how these key steps in the design thinking process transform abstract ideas into tangible realities that make a meaningful impact on the world. Join us as we journey deeper into the heart of design thinking, where creativity knows no bounds and innovation knows no limits.
Step 4: Prototyping – Bringing Ideas to Life
In the dynamic world of design thinking, prototyping serves as the bridge between abstract ideas and tangible realities. It’s the stage where concepts take shape, where imagination meets practicality, and where innovation comes to life.
Prototype Stage: Prototyping is not just about creating a mere representation of a solution; it’s about crafting a tangible embodiment of ideas that can be interacted with and tested. From simple sketches to sophisticated digital mock-ups, prototypes come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose in the design process.
Prototypes allow design teams to explore different design directions, experiment with functionality, and gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and end-users. By bringing ideas out of the realm of abstraction and into the realm of reality, prototypes provide a concrete platform for discussion, iteration, and refinement.
Testing Phase: The true value of a prototype lies not in its aesthetics or polish but in its ability to facilitate meaningful testing and evaluation. Through user testing and feedback sessions, design teams can gain insights into how users interact with the prototype, what works well, and what needs improvement.
User testing serves as a reality check, helping teams identify usability issues, uncover unmet needs, and validate design assumptions. By observing users in real-world scenarios, design teams can gain a deeper understanding of user behavior, preferences, and pain points, guiding the iterative process of refinement and improvement.
Iterative Process: Design thinking is inherently iterative, and the prototyping stage is no exception. It’s not uncommon for prototypes to undergo multiple iterations, each building upon the insights gained from previous testing rounds.
The iterative nature of prototyping allows design teams to fail fast and learn quickly, iterating on ideas and incorporating feedback until the optimal solution is achieved. This iterative approach not only ensures that the final product meets user needs but also minimizes the risk of costly mistakes during the development process.
Step 5: Testing and Iteration – Refining Solutions
Testing and iteration are the engines that drive the refinement of solutions in the design thinking process. It’s where ideas are put to the test, where assumptions are challenged, and where breakthroughs are born.
User Testing: User testing is the cornerstone of effective design. By observing how real users interact with prototypes, design teams gain valuable insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points. This firsthand feedback guides the iterative process of refinement and improvement.
User testing provides an opportunity to validate design decisions, identify usability issues, and uncover unforeseen challenges. By involving end-users early and often in the testing process, design teams can ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations.
Iterative Approach: Iteration is not a sign of failure but rather a testament to the iterative nature of design thinking. It’s about embracing feedback, learning from mistakes, and continuously refining solutions until the best possible outcome is achieved.
Each iteration builds upon the insights gained from previous testing rounds, bringing design teams one step closer to the optimal solution. Through a process of continuous learning and adaptation, design teams can navigate the complexities of problem-solving with confidence and agility.
Continuous Learning: Testing and iteration are not one-time events; they are ongoing processes of discovery and improvement. Each round of testing provides new insights, new challenges, and new opportunities for innovation.
By fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement, design teams can stay agile, responsive, and adaptive in the face of evolving user needs and market dynamics.
In the subsequent sections, we’ll explore how these key steps in the design thinking process pave the way for the implementation of innovative solutions that address real problems and meet the needs of users. Join us as we journey deeper into the heart of design thinking, where creativity knows no bounds and where every challenge is an opportunity for growth and discovery.
Implementation: Turning Ideas into Reality
As the design thinking process nears its culmination, the focus shifts from ideation and prototyping to the pivotal stage of implementation. Implementation is where the rubber meets the road, where innovative ideas are transformed into tangible solutions that address real-world problems and meet the needs of users.
Product Development: Implementation involves translating conceptual designs and prototypes into fully functional products or services. This stage requires a concerted effort from cross-functional teams, including designers, engineers, marketers, and product managers, to bring the vision to fruition.
Aligning with Business Goals: Successful implementation requires alignment with overarching business goals and objectives. Solutions must not only meet user needs but also contribute to the organization’s strategic priorities, whether it’s driving revenue growth, enhancing customer satisfaction, or fostering innovation.
Iterative Refinement: Implementation is not a one-time event but rather a series of iterative refinements aimed at optimizing the solution over time. Continuous feedback loops, user testing, and performance metrics enable teams to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to enhance usability, functionality, and overall user experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the design thinking process offers a systematic yet flexible framework for addressing complex problems and generating innovative solutions that resonate with users and stakeholders alike. By prioritizing human needs, embracing a user-centered approach, and fostering collaboration and creativity, design teams can navigate the challenges of problem-solving with confidence and clarity.
Throughout the various stages of the design thinking process—from understanding the problem and generating ideas to prototyping, testing, and implementation—key principles such as empathy, iteration, and user-centricity guide the way. As advocated by thought leaders like Tim Brown and institutions like Stanford University, design thinking is not just a methodology but a mindset—a way of approaching problems and opportunities with curiosity, empathy, and a relentless pursuit of excellence.
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, where the pace of change is accelerating and the challenges we face are increasingly complex, the principles and practices of design thinking offer a beacon of hope and a pathway to progress. By embracing the principles of human-centered design, fostering a culture of innovation, and harnessing the power of collaborative problem-solving, organizations can unlock new insights, create meaningful experiences, and drive positive change in the world.
As we look to the future, let us continue to embrace the principles of design thinking, harnessing the power of creativity, empathy, and collaboration to tackle the most pressing challenges of our time and create a brighter, more inclusive, and more sustainable world for generations to come.
Explore Our Latest Articles
Want to present your work in an Incredible way?
Integrate your designs and images into your website with our WordPress Aeroscroll Gallery plugin!

Aeroscroll Gallery is a dynamic WordPress plugin designed to elevate your website’s visual experience. It seamlessly integrates with your WordPress site, offering customizable and responsive photo galleries with smooth scrolling effects. With Aeroscroll Gallery, effortlessly showcase your images in an engaging and interactive manner, enhancing user engagement and aesthetics.

Learn More here: https://www.aeroscroll.com
Demos: /essential-gallery-demos/